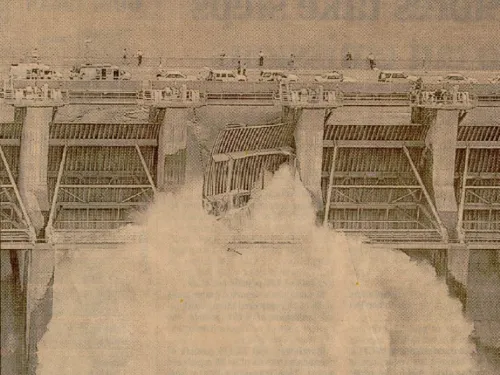
Regular operation, maintenance, and inspection of dams is important to the early detection and prevention of dam failure.
Regular operation and maintenance as well as thorough and consistent inspection must be practiced throughout the lifetime of a dam. In addition to maintaining proper function, cost efficiency, and compliance with safety regulations, such habits can lead to the early detection of deficiencies and prevention of failure. Continuing these management activities is a simple way to extend the useful life of a dam provided a detailed Operations and Maintenance (O&M) Program that includes routine, adequate inspections has been developed and is followed.

An O&M Plan is a unique guidance document developed to ensure that a dam is performing safely and according to its design and purpose. As the name suggests, this type of program contains details pertaining to two main administrative matters: operation and maintenance. The first portion of an O&M Plan consists of a series of procedures that are essential to proper dam operation and often extracted from a Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) report or a similar type of manual. This section of an O&M Plan may also contain managerial practices to guarantee and document the completion of the SOPs.
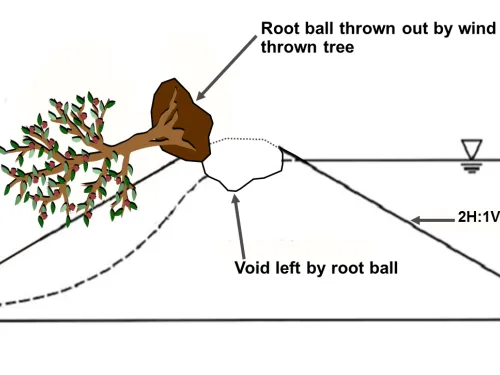
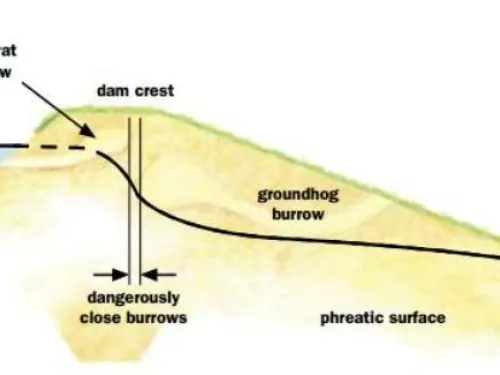
While the first part of an O&M Plan is devoted to dam operations, the second focuses on facility upkeep. Standard practices for both preventive and extraordinary maintenance should be provided in this section. Preventative maintenance is performed routinely and includes the servicing of the dam and its appurtenances with the intention of avoiding over-vegetation, animal impacts, equipment deterioration, mechanical malfunction, flooding, or failure. Extraordinary maintenance is comprised of the repairs required to correct these damages if they do occur.
In addition to consistent and documented operation and maintenance, regular inspection is essential to preserving the proper functionality of a dam. Formal dam safety inspections and routine assessments should be conducted regularly. Dam assessments are thorough investigations of a dam by licensed professionals in which design documents are consulted and the current conditions are compared to those considered state-of-the-art. Inspections are conducted on a more frequent basis by dam operators or maintenance personnel. These inspections include simple observation of the dam, appurtenances, the reservoir, and surrounding area.
With the implementation of consistent operation, maintenance, and inspection comes a record of baseline conditions at the dam. As a result, deviation from normalcy becomes apparent. Because signs of potential risk and failure often present themselves prior to a disaster, early detection of such issues through proper O&M and inspection is essential. Early detection of potential dam incidents provides crucial time for the appropriate response to be executed. When performed according to O&M documents and immediately following an unusual observation, these two actions can lead to the prevention of dam failure and its consequences.
References:
(1) USBR. (1990). Training Aids for Dam Safety: How to Organize an Operation and Maintenance Program. US Bureau of Reclamation.





Baldwin Hills Dam (California, 1963)

Barahona No. 1 Dam (Chile, 1928)

Big Bay Lake Dam (Mississippi, 2004)

Buffalo Creek Dam (West Virginia, 1972)

Camará Dam (Brazil, 2004)

Canyon Lake Dam (South Dakota, 1972)

Castlewood Canyon Dam (Colorado, 1933)

Columbia River Levees at Vanport (Oregon, 1948)

Folsom Dam (California, 1995)

Ka Loko Dam (Hawaii, 2006)

Kelly Barnes Dam (Georgia, 1977)

Lake Delhi Dam (Iowa, 2010)

Laurel Run Dam (Pennsylvania, 1977)

Lawn Lake Dam (Colorado, 1982)

Maple Grove Dam (Colorado, 1979)

Marshall Lake Dam (Colorado)

Penn Forest Dam (Pennsylvania, 1994)

Quail Creek Dike (Utah, 1989)

Santa Clara Dam (Utah, 2012)

South Fork Dam (Pennsylvania, 1889)

St. Francis Dam (California, 1928)

Taum Sauk Dam (Missouri, 2005)

Tempe Town Lake Dam (Arizona, 2010)

Toddbrook Reservoir Dam (England, 2019)

Tous Dam (Spain, 1982)

Val di Stava Dam (Italy, 1985)

Abu Mansour & Al-Bilad Dams (Libya, 2023)

Feijão Dam B-1 (Brazil, 2019)

Harmony Gold Mine No. 4 Tailings Dam (South Africa, 1994)

Bonasa Breaks Ranch Dam (Washington, 2017)
Additional Case Studies (Not Yet Developed)
- Black Creek Site 53 (Mississippi, 1983)
- Centennial Narrows Dam (Arizona, 1997)
- Lake Needwood Dam (Maryland, 2006)

Evaluation and Monitoring of Seepage and Internal Erosion

Model State Dam Safety Program Manual

Technical Manual for Dam Owners: Impacts of Animals on Earthen Dams

Technical Manual for Dam Owners: Impacts of Plants on Earthen Dams

Training Aids for Dam Safety: Dam Safety Awareness

Training Aids for Dam Safety: Documenting and Reporting Findings from a Dam Safety Inspection

Training Aids for Dam Safety: How to Organize a Dam Safety Program

Training Aids for Dam Safety: How to Organize an Operation and Maintenance Program

Training Aids for Dam Safety: Identification of Material Deficiencies

Training Aids for Dam Safety: Identification of Visual Dam Safety Deficiencies

Training Aids for Dam Safety: Inspection and Testing of Gates, Valves, and Other Mechanical Systems
Training Aids for Dam Safety: Inspection of Concrete and Masonry Dams

Training Aids for Dam Safety: Inspection of Embankment Dams

Training Aids for Dam Safety: Inspection of Spillways and Outlet Works

Training Aids for Dam Safety: Inspection of the Foundation, Abutments, and Reservoir Rim

Training Aids for Dam Safety: Preparing to Conduct a Dam Safety Inspection

Maintenance and Operation of Dams to Prevent Failure

Pocket Safety Guide for Dams and Impoundments